The blockchain is the new hot technology. If you haven’t heard about it, you probably know Bitcoin. Well, the blockchain is the underlying technology that powers Bitcoin. Experts say the blockchain will cause a revolution similar to what Internet provoked. But what is it really, and how can it be used to build apps today? This post is the first in a series of three, explaining the blockchain phenomenon to web developers. We’ll discuss the theory, show actual code, and share our learnings, based on a real world project.
To begin, let’s try to understand what blockchains really are.
What Is A Blockchain, Take One
Although the blockchain was created to support Bitcoin, the blockchain concept can be defined regardless of the Bitcoin ecosystem. The literature usually defines a blockchain as follows:
A blockchain is a ledger of facts, replicated across several computers assembled in a peer-to-peer network. Facts can be anything from monetary transactions to content signature. Members of the network are anonymous individuals called nodes. All communication inside the network takes advantage of cryptography to securely identify the sender and the receiver. When a node wants to add a fact to the ledger, a consensus forms in the network to determine where this fact should appear in the ledger; this consensus is called a block.
I don’t know about you, but after reading these definitions, I still had troubles figuring out what this is all about. Let’s get a bit deeper.
Ordering Facts
Decentralized peer-to-peer networks aren’t new. Napster and BitTorrent are P2P networks. Instead of exchanging movies, members of the blockchain network exchange facts. Then what’s the real deal about blockchains?
P2P networks, like other distributed systems, have to solve a very difficult computer science problem: the resolution of conflicts, or reconciliation. Relational databases offer referential integrity, but there is no such thing in distributed system. If two incompatible facts arrive at the same time, the system must have rules to determine which fact is considered valid.
Take for instance the double spend problem: Alice has 10$, and she sends twice 10$ to Bob and Charlie. Who will have the 10$ eventually? To answer this question, the best way is to order the facts. If two incompatible facts arrive in the network, the first one to be recorded wins.
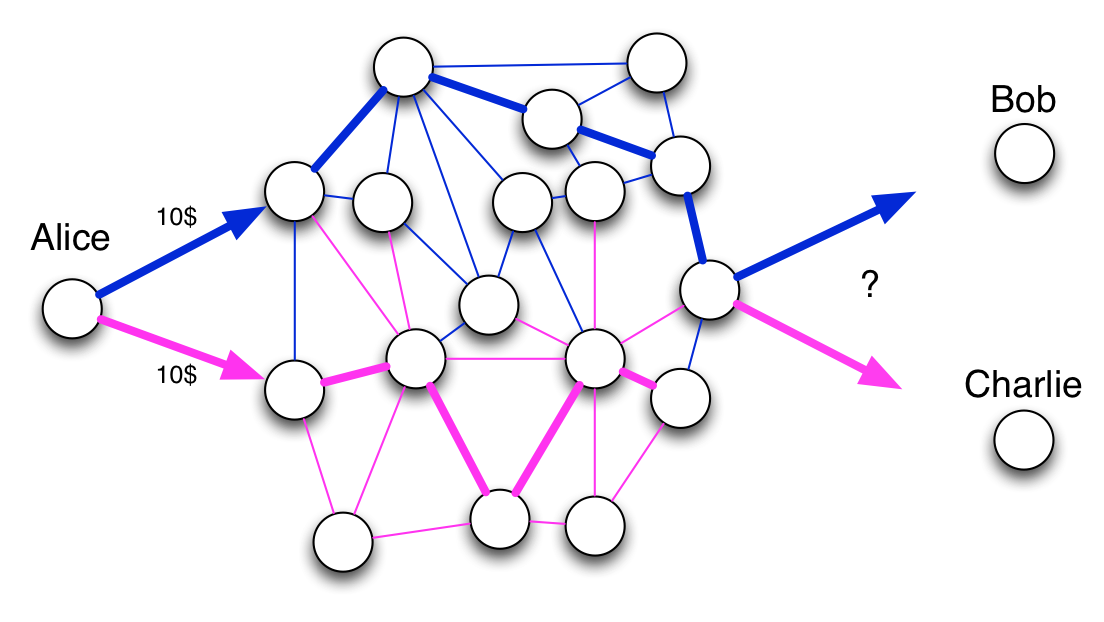
In a P2P network, two facts sent roughly at the same time may arrive in different orders in distant nodes. Then how can the entire network agree on the first fact? To guarantee integrity over a P2P network, you need a way to make everyone agree on the ordering of facts. You need a consensus system.
Consensus algorithms for distributed systems are a very active research field. You may have heard of Paxos or Raft algorithms. The blockchain implements another algorithm, the proof-of-work consensus, using blocks.
Blocks
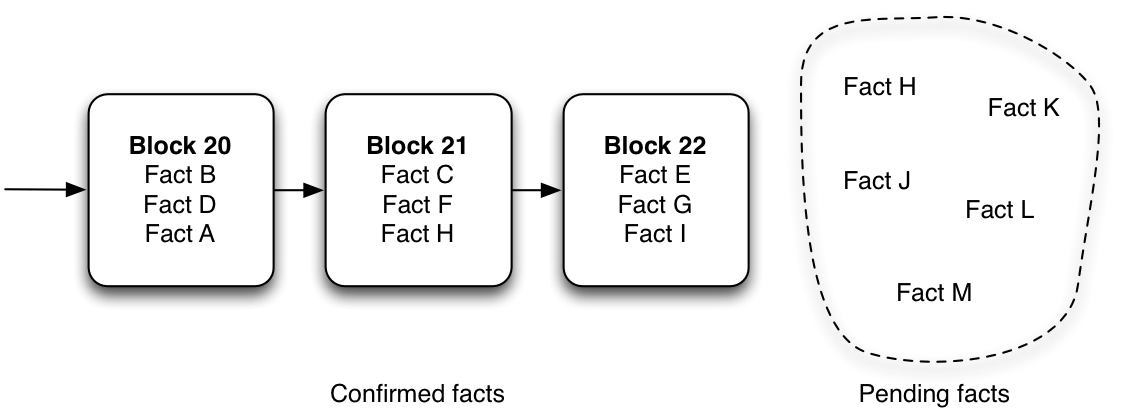
Blocks are a smart trick to order facts in a network of non-trusted peers. The idea is simple: facts are grouped in blocks, and there is only a single chain of blocks, replicated in the entire network. Each block references the previous one. So if fact F is in block 21, and fact E is in block 22, then fact E is considered by the entire network to be posterior to fact F. Before being added to a block, facts are pending, i.e. unconfirmed.
Mining
Some nodes in the chain create a new local block with pending facts. They compete to see if their local block is going to become the next block in the chain for the entire network, by rolling dice. If a node makes a double six, then it earns the ability to publish their local block, and all facts in this block become confirmed. This block is sent to all other nodes in the network. All nodes check that the block is correct, add it to their copy of the chain, and try to build a new block with new pending facts.
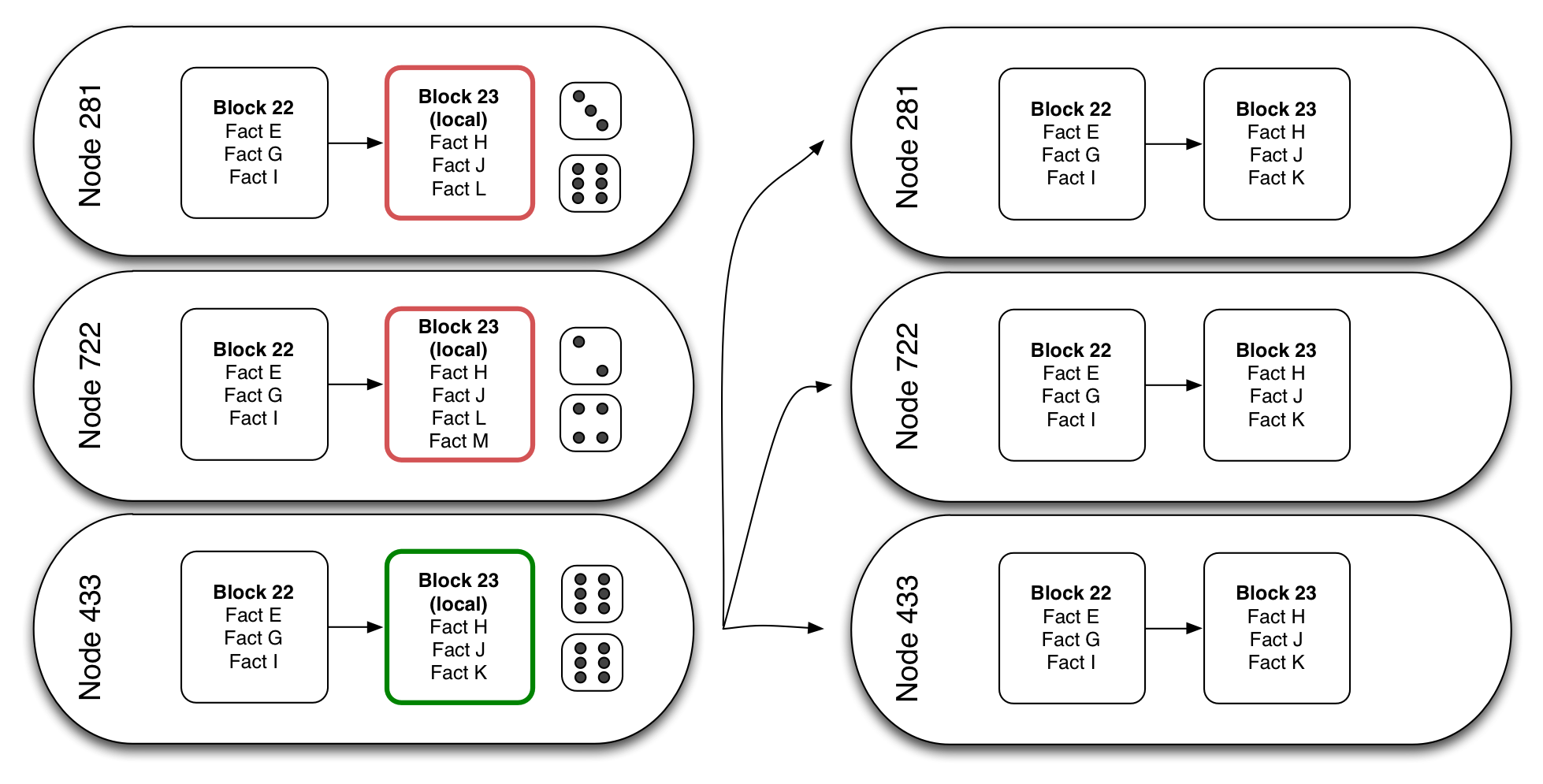
But nodes don’t just roll a couple dice. Blockchain challenges imply rolling a huge number of dice. Finding the random key to validate a block is very unlikely, by design. This prevents fraud, and makes the network safe (unless a malicious user owns more than half of the nodes in the network). As a consequence, new blocks gets published to the chain at a fixed time interval. In Bitcoin, blocks are published every 10 minutes on average.
In Bitcoin, the challenge involves a double SHA-256 hash of a string made of the pending facts, the identifier of the previous block, and a random string. A node wins if their hash contains at least n leading zeroes.
// a losing hash for Bitcoin 787308540121f4afd2ff5179898934291105772495275df35f00cc5e44db42dd // a winning hash for Bitcoin if n=10 00000000009f766c17c736169f79cb0c65dd6e07244e9468bc60cde9538b551eNumber n is adjusted every once in a while to keep block duration fixed despite variations in the number of nodes. This number is called the difficulty. Other blockchain implementations use special hashing techniques that discourage the usage of GPUs (e.g. by requiring large memory transfers).
The process of looking for blocks is called mining. This is because, just like gold mining, block mining brings an economical reward – some form of money. That’s the reason why people who run nodes in a blockchain are also called miners.
Note: By default, a node doesn’t mine – it just receives blocks mined by other nodes. It’s a voluntary process to turn a node into a miner node.
Money and Cryptocurrencies
Every second, each miner node in a blockchain tests thousands of random strings to try and form a new block. So running a miner in the blockchain pumps a huge amount of computer resources (storage and CPU). That’s why you must pay to store facts in a blockchain. Reading facts, on the other hand, is free: you just need to run your own node, and you’ll recuperate the entire history of facts issued by all the other nodes. So to summarize:
- Reading data is free
- Adding facts costs a small fee
- Mining a block brings in the money of all the fees of the facts included in the block
We’re not talking about real money here. In fact, each blockchain has its own (crypto-)currency. It’s called Bitcoin (BTC) in the Bitcoin network, Ether (ETH) on the Ethereum network, etc. To make a payment in the Bitcoin network, you must pay a small fee in Bitcoins – just like you would pay a fee to a bank. But then, where do the first coins come from?
Miners receive a gratification for keeping the network working and safe. Each time they successfully mine a block, they receive a fixed amount of cryptocurrency. In Bitcoin this gratification is 25 BTC per block, in Ethereum it’s 5 ETH per block. That way, the blockchain generates its own money.
Lastly, cryptocurrencies rapidly became convertible to real money. Their facial value is only determined by offer and demand, so it’s subject to speculation. At the time of writing, mining Bitcoins still costs slightly less in energy and hardware than you can earn by selling the coins you discovered in the process. That’s why people add new miners every day, hoping to turn electricity into money. But fluctuations in the BTC value make it less and less profitable.
Contracts
So far we’ve mostly mentioned facts storage, but a blockchain can also execute programs. Some blockchains allow each fact to contain a mini program. Such programs are replicated together with the facts, and every node executes them when receiving the facts. In bitcoin, this can be used to make a transaction conditional: Bob will receive 100 BTC from Alice if and only if today is February 29th.
Other blockchains allow for more sophisticated contracts. In Ethereum for instance, each contract carries a mini-database, and exposes methods to modify the data. As contracts are replicated across all nodes, so are their database. Each time a user calls a method on the contract and therefore updates the underlying data, this command is replicated and replayed by the entire network. This allows for a distributed consensus on the execution of a promise.
This idea of pre-programed conditions, interfaced with the real world, and broadcasted to everyone, is called a smart contract. A contract is a promise that signing parties agree to make legally-enforceable. A smart contract is the same, except with the word “technically-“ instead of “legally-“. This removes the need for a judge, or any authority acknowledged by both parties.
Imagine that you want to rent your house for a week and $1,000, with a 50% upfront payment. You and the loaner sign a contract, probably written by a lawyer. You also need a bank to receive the payment. At the beginning of the week, you ask for a $5,000 deposit; the loaner writes a check for it. At the end of the week, the loaner refuses to pay the remaining 50%. You also realize that they broke a window, and that the deposit check refers to an empty account. You’ll need a lawyer to help you enforce the rental contract in a court.
Smart contracts in a blockchain allow you to get rid of the bank, the lawyer, and the court. Just write a program that defines how much money should be transferred in response to certain conditions:
- two weeks before beginning of rental: transfer $500 from loaner to owner
- cancellation by the owner: transfer $500 from owner to loaner
- end of the rental period: transfer $500 from loaner to owner
- proof of physical degradation after the rental period: transfer $5,000 from loaner to owner
Upload this smart contract to the blockchain, and you’re all set. At the time defined in the contract, the money transfers will occur. And if the owner can bring a predefined proof of physical degradation, they get the $5,000 automatically (without any need for a deposit).
You might wonder how to build a proof of physical degradation. That’s where the Internet of Things (IoT) kicks in. In order to interact with the real world, blockchains need sensors and actuators. The Blockchain revolution won’t happen unless the IoT revolution comes first.
Such applications relying on smart contracts are called Decentralized Apps, or DApps.
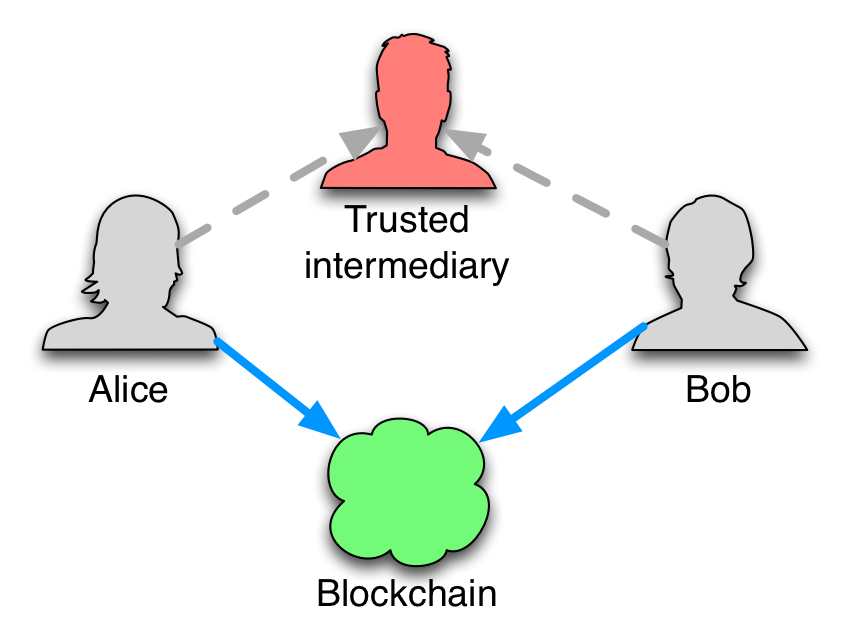
Smart contracts naturally extend to smart property, and a lot more smart things. The thing to remember is that “smart” means “no intermediaries”, or “technically-enforced”. Blockchains are a new way to disintermediate businesses – just like the Internet disintermediated music distribution.
Tag: web development in blockchain, how does the blockchain work, blockchain data structure, how does blockchain work, blockchain news, how blockchain works, blockchain database, blockchain technology, blockchain applications, blockchain explained, blockchain, what is a blockchain, blockchain com, blockchain app, what is the blockchain, sidechain. what is sidechain, sidechain blockchain, blockstream sidechain, what is blockstream

Hitesh Malviya is the Founder of ItsBlockchain. He is one of the most early adopters of blockchain & cryptocurrency enthusiast in India. After being into space for a few years, he started IBC in 2016 to help other early adopters learn about the technology.
Before IBC, Hitesh has founded 4 companies in the cyber security & IT space.
Subscribe to get notified on latest posts.